Avian Influenza
Avian Influenza
Profile
Avian influenza (also known as bird flu) is a notifiable viral disease of birds. The pathogens are influenza A viruses, which are divided into subtypes based on different surface antigens (haemagglutinin, HA and neuraminidase, NA). In birds, there are currently 16 haemagglutinin and 9 neuraminidase subtypes. New virus variants are constantly emerging as a result of genetic changes and the exchange of genetic material.
A distinction can be made between highly pathogenic (highly pathogenic, HPAIV) and low pathogenic (low pathogenic, LPAIV) avian influenza viruses. The distinction is based on the severity of the disease in birds. Highly pathogenic for birds are some variants of the subtypes H5 and H7. These viruses are highly infectious for birds, and clinical illnesses in poultry are also referred to as avian influenza. Low pathogenic variants of the avian influenza virus can spontaneously change into highly pathogenic virus variants through mutations and thus cause severe outbreaks of disease.
Mammals (including pigs, horses, cats, dogs, foxes, badgers, martens, otters and minks) can also become infected with avian influenza viruses and fall ill. Since the beginning of 2024, infections in cattle and goats with influenza A(H5N1) have also been detected in the USA for the first time. People who had close contact with these animals also fell ill in individual cases. There was no human-to-human transmission. In other parts of the world, sporadic transmissions of avian influenza to humans have been reported, some of which can lead to fatal illnesses. Almost all human infections are due to close direct contact with infected or sick poultry or indirectly via their faeces. Human-to-human transmission has not yet been observed worldwide. The subtype (A)H5N1 currently occurring in Europe is poorly adapted to humans and disease has not yet been observed in Europe.
Route of infection
All poultry species, but also many species of ornamental birds, birds of prey and wild birds are susceptible to avian influenza viruses. The HPAI viruses are highly infectious, especially for poultry. The virus is excreted in faeces, saliva and tear fluid. Infection occurs directly from animal to animal or indirectly via objects that have come into contact with the virus. If there is a lot of dust, indirect infection via the air is also possible.
Humans and other mammals (including pigs, cattle, goats, cats, dogs, foxes, badgers, martens, otters and minks) can also become infected with avian influenza viruses through intensive contact with infected poultry.
Symptomatology
While low-pathogenic AI viruses cause no or only mild symptoms, infections with highly pathogenic AI variants lead to severe courses of disease and high mortality rates. Chickens, turkeys and numerous wild bird species are particularly affected. Respiratory symptoms up to severe respiratory distress, greenish watery diarrhea, bleeding on organs, encephalitis (CNS symptoms), comb tips and stands, edema (swelling) in the head area, pronounced decrease in laying performance, thin and missing egg shells, significantly reduced water and feed intake, languor and fever are common symptoms of an illness with the highly pathogenic avian influenza virus. Ducks, geese, and some wild bird species usually show no or only mild symptoms, but are important for pathogen spread.
In mammals, infection with avian influenza viruses is often asymptomatic or with mild flu-like symptoms. However, infections with certain HPAIV variants can also lead to severe and fatal disease.
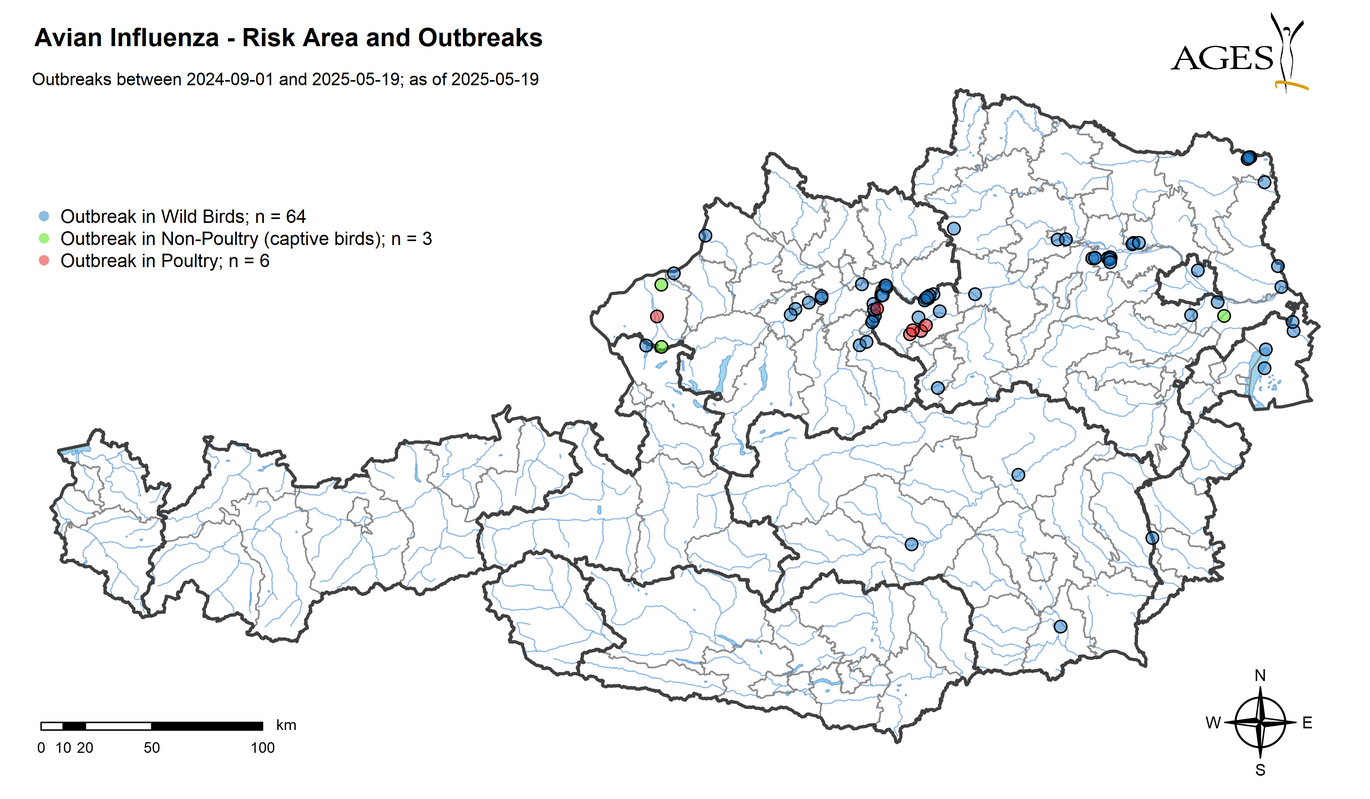
Following several outbreaks of highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) subtype H5N1 in wild birds, poultry farms and hobby farms last autumn and winter, the outbreak situation has eased significantly. Poultry farms and captive bird holdings have not been affected for several months, while wild birds are currently only affected in very isolated cases.
As of 10 May 2025, there are therefore no longer any areas with an increased risk of poultry plague in the entire federal territory.
Information from the Ministry of Health on avian influenza
Information on the international situation and spread of HPAI is evaluated and compiled in the monthly Animal Disease Radar Austria.
Poultry farmers should ensure that biosecurity measures are observed: direct and indirect contact between poultry and wild birds should be prevented as far as possible. In the event of health problems in poultry farms, a veterinary examination should be carried out and avian influenza should be ruled out. For early detection and prevention of further spread, all wild waterfowl and birds of prey found dead must be reported to the locally competent district administrative authority (official veterinarian). Such animals should not be touched and should be left where they are found. The authorities will arrange for the animals to be recovered and examined.
Given the occasion, we would also like to point out that every poultry farm must be reported to the competent district administrative authority
Notification of poultry farming in the Consumer Health Information System (VIS)
Avian influenza surveillance in Austria
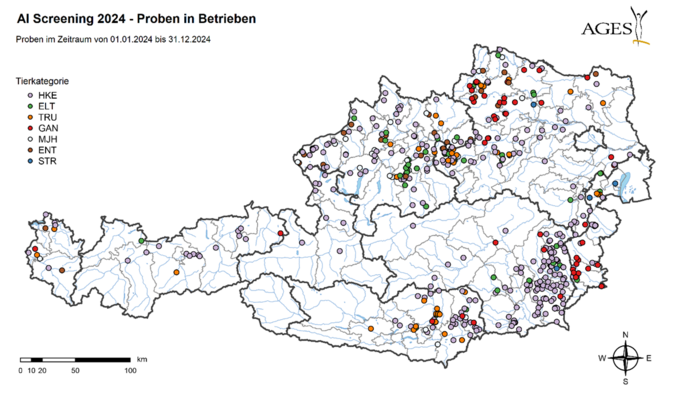
The Europe-wide AI surveillance programme consists of an active part (productive poultry) and a passive part (wild birds). As part of suspected cases, re-housing, clarification and exclusion tests, additional samples from poultry farms and hobby farms are also tested for the presence of avian influenza viruses using PCR.
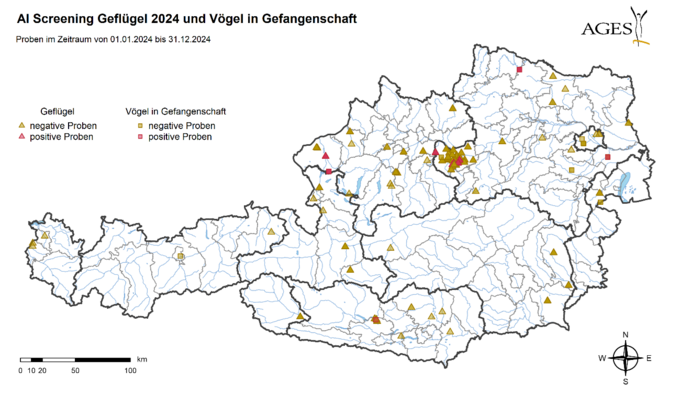
As part of the active surveillance programme, a total of 6,481 poultry blood samples were tested for the avian influenza virus in Austria in 2024. Slaughter blood from 3,675 laying hens from 332 farms (including 254 free-range farms), from 543 parent birds from 52 farms, from 540 fattening turkeys from 45 farms, from 842 geese and 940 ducks from 92 farms and from 31 ostriches from 8 farms was tested serologically using the Elisa test. No antibodies against influenza A virus subtypes H5 and/or H7 were detected.
897 samples from poultry and captive birds were tested for the AI virus genome as part of clarification tests. Highly pathogenic AI virus (HPAIV) of subtype H5N1 was detected in 6 poultry farms in the districts of Braunau am Inn and Amstetten and in 4 hobby farms in the districts of Villach-Land, Horn, Braunau am Inn and Bruck an der Leitha.
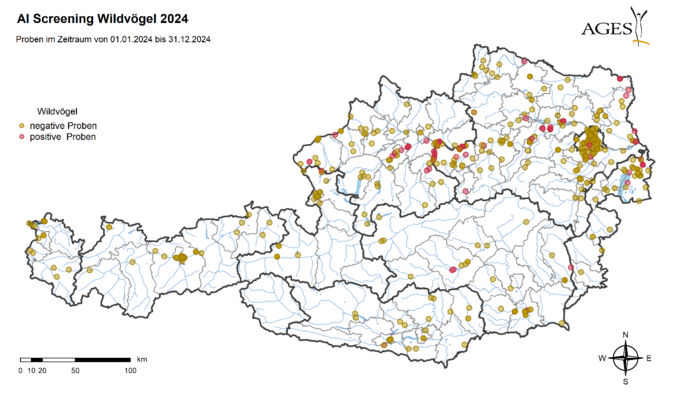
As part of passive surveillance in 2024, 600 samples of wild birds found dead were analysed for the avian influenza A virus genome using PCR. The highly pathogenic A(H5N1) virus of subtype 2.3.4.4b was detected in 107 dead wild birds from 7 federal provinces (Tyrol and Vorarlberg not affected).
At the National Reference Laboratory for Avian Influenza (NRL, AGES Mödling), we test various bird samples (organs, swabs, carcasses) for the presence of AIV using Influenza A real-time RT-PCR. Positive detections are further subtyped and confirmed by sequencing, egg culture and hemagglutination test (HA). Indirect detection by determination of antibodies is performed by ELISA and hemagglutination inhibition test (HAH).
Real-time RT-PCR and sequencing: Influenza A viruses are tested molecularly in all birds by real-time RT-PCR. If positive, AIV variants are typed directly using specific methods to determine whether an H5 or H7 subtype is present. The NRL can currently differentiate all H1 to H16 or N1 to N9 AIV subtypes. Sanger DNA sequencing can be used to determine the pathotype of the H5 or H7 virus strain (low pathogenic or high pathogenic, LPAI or HPAI). Whole-genome sequencing is performed on selected samples, where all eight segments of the viral genome are enriched and subsequently sequenced. Enrichment is performed directly from clinical samples using a dedicated RT-PCR, and sequencing is performed using modern high-throughput equipment (next generation sequencing).
Hemagglutination test: Certain viruses, such as influenza A viruses, bind erythrocytes to their surface using hemagglutinin. This causes the blood to agglutinate (clump together). Dilution series can be used to determine the amount of virus.
Hemagglutination inhibition test: Special antibodies can prevent the agglutination (clumping) caused by the virus. In this way, antibody titers and specific antibodies directed against individual AI virus strains can be determined.
ELISA: The Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay is an antibody-based detection method. Antibodies present in serum bind to a specific antigen and are measured qualitatively or semi-quantitatively using an enzymatic color reaction.
Egg culture: a potentially infectious inoculum solution is prepared from the samples, with which guaranteed virus-free chicken eggs are inoculated. These eggs are incubated for at least five days. If highly pathogenic HPAI viruses are present, the embryos in the eggs die and the virus in the allantios can be identified by hemagglutination (HA).
Contact
Institut für veterinärmedizinische Untersuchungen Mödling
- vetmed.moedling@ages.at
- +43 50 555-38112
-
Robert Koch-Gasse 17
2340 Mödling
Last updated: 26.05.2025
automatically translated