Ascochyta blight on pea
Ascochyta pisi, Ascochyta pinodes, Ascochyta pinodella
Damage symptoms
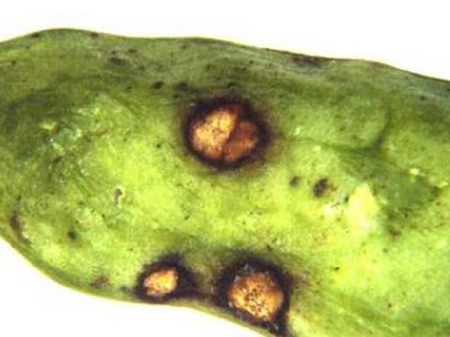
Different symptoms can be visible on the leaves and pods. On the one hand, these can be reddish-brown, not sunken and blurred spots, which are up to 7 mm in size. On the other hand, they may be roundish, light brown, sunken spots surrounded by a dark, raised border (focal spots, up to 1 cm in size), which may also have dark spore containers (pycnidia) in the spots. This symptom of pest is very characteristic of burn spot disease of pea.


Prevention and control
- Use of tested and healthy seeds
- Cultivation of peas on heavily infected sites in wide crop rotation
- dressing with a special dressing agent, as the pathogen grows deep in the grain (see list of plant protection products approved in Austria)
Last updated: 10.04.2025
automatically translated