Common thorn apple
Datura stramonium
Appearance
The leaves of the common datura are dark green on top, long-stalked, ovate, pointed, lobed and sometimes very large (20 cm in diameter). The species is characterized by a great variability in appearance. Depending on nutrient, water, and competition conditions, growth height at seed maturity can vary from a few centimeters to more than 150 cm.
The trumpet flowers stand upright in the branch forks. From them a characteristic densely spiny, walnut-sized capsule is formed, in which deep brown to black seeds are found.



Distribution
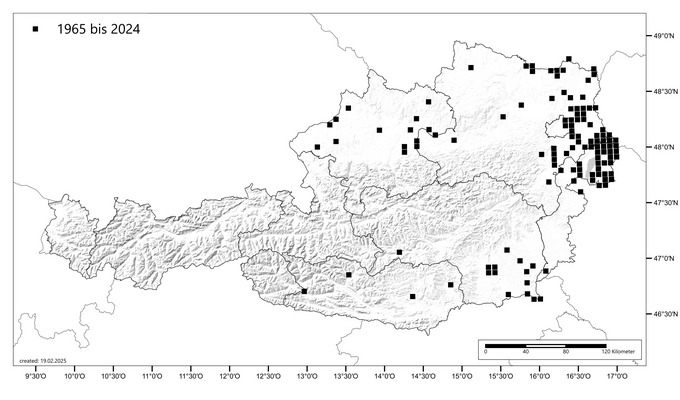
The common datura occurs in all federal states. The plant mainly colonises nutrient-rich ruderal areas (e.g. rubbish tips, compost heaps, urban wasteland) and fields.
The species has only become an important weed in recent decades. An increased occurrence was first observed in the 1990s. The "hotspots" of datura in agriculture are currently located in the warm lowlands of northern Burgenland and eastern Lower Austria. In southern and south-eastern Styria and in Upper Austria, occurrences have been observed in the fields in recent years. There are only isolated records in fields in Carinthia. Further west, no occurrences in fields have been described to date.
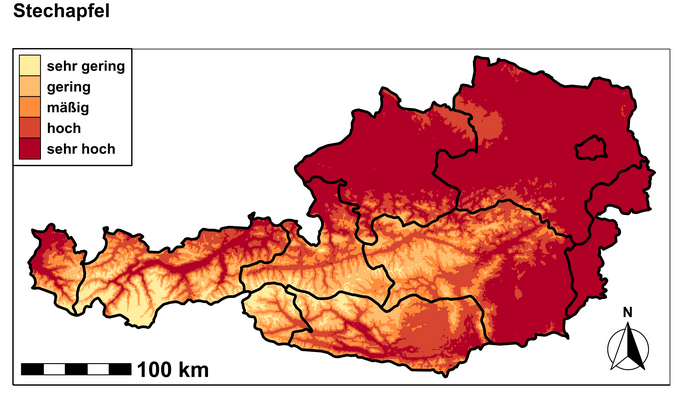
The area of Austria that is highly to very highly suitable for datura under the current climatic conditions is over 70 % and covers more than 90 % of arable land.
Spread and transmission
- Natural dispersal: Seeds are dispersed from the capsules when they burst and also by wind movements up to a distance of 1 to 3 metres from the mother plant.
- Anthropogenic dispersal: Seeds are spread over long distances with the help of agricultural equipment and harvesting machines.
Economic significance
As a heat germinator, datura emerges relatively late and can therefore be found in fields, particularly in summer annual crops such as maize, soya beans, potatoes, sunflowers and millet, but also in field vegetables.
Especially in field crops with a low growth height, the common datura can develop enormous competitive power and cause high yield losses. A much more problematic aspect is that the entire plant is highly toxic, as it contains organic compounds(tropane alkaloids). Contamination occurs when the harvested crop comes into contact with plant parts and plant juices of the (green) datura during harvesting. Relatively small amounts of these alkaloids can lead to poisoning (sensory illusions, nausea, drowsiness, respiratory paralysis) if ingested with food.
Prevention and control
Indirect and direct measures
- Use of accompanying measures, e.g. alternating winter and summer crops, checking the edges and transitional areas of the fields (field margins, fallow land)
- Mechanical weed control with harrow and hoe. The harrow only has an effect on small individuals. Coulter hoes also capture larger plants. Specimens in the row are often poorly controlled.
- Selection and use of effective herbicides in the crops(list of plant protection products authorised in Austria)
Checking the crops
- Inspection before the crop closes, but at the latest before harvest: individuals must be removed before seed formation.
- Removal of individual plants or smaller populations is best done by pulling out or digging up. Disposal: Do not leave plants at the edge of the field, but put them in rubbish bags and dispose of them with the residual waste. Larger quantities can be sent to professional composting or biogas plants.
Specialist information
Follak S, Essl F, Glaser M, Hörmann GM (2025): Potenzielle Verbreitungsgebiete wichtiger Problemunkräuter. Der Pflanzenarzt 78(5) (im Druck).
Follak S, Reiter E, Riegler-Nurscher P, Treiblmeier M (2024): Datura - a late problem. Landwirt 12/2024, 46-47.
Follak S, Reiter E, Riegler-Nurscher P, Treiblmeier M (2024): Datura detection using drones. The plant doctor 77(6-7), 14-15.
Follak S, Hochfellner L, Schwarz M (2023): Watch out! Datura is becoming more and more of a problem. The plant doctor 76 (6-7), 30-31.
Last updated: 22.05.2025
automatically translated